Helpful Advice for
Buying Your Home
A Homebuyer's Guide to
Guide to Credit Scores
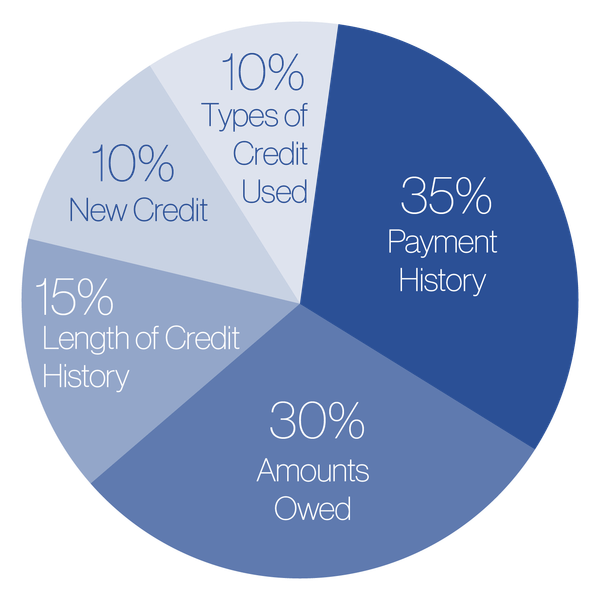
Specific Actions that REDUCE Credit Score:
So many extremely responsible people have credit scores that may not accurately reflect their credit worthiness. We may unwittingly do some of the following things that may ultimately hurt our credit scores:
- Open new credit card accounts to transfer balances to lower rate cards
- Close old accounts so that the average age of open accounts is less than 5 years
- Apply for a few loans, hoping to shop around for the best rate
- Open retail credit accounts to receive discounts
- Keep overall credit balances low, but have one account with a high credit ratio
- Close a credit card account before paying off the balance in full
- Have many open credit accounts - even if they have zero or low balances
- Not making payments on time; skipping a month, paying late, or paying less than the minimum monthly payment
- Allowing a disputed charge go to collections, rather than correct it
Specific Actions to IMPROVE Credit Score:
Here are a few practices that you can start doing to make sure that score keeps trending upward.
- Make at least the minimum monthly payments on time, ever time
- Do not let credit accounts go to a collection department or be sold to a collection company
- Limit the number of open credit accounts to between 3 and 5
- Keep credit balances low (or zero) on all open accounts
- Try to keep old credit card accounts open
- Keep credit inquiries to a minimum
850-720:
Excellent
It is estimated that slightly less than 50% of the population has an excellent credit score. This is a group of people who have generally been at their current job (or current line of work) for more than 2 years. These people pay at least the minimum payments on their debts on time every month. These people generally carry a balance of less than 30% of their available revolving credit (i.e. credit cards), and they do not open new credit accounts frequently, or have many credit inquires.
719-680:
Good
This group contains approximately 15% of the population. These people may be doing almost everything right, but have a lowered score because one or more minor issues. Perhaps one of their credit cards has a high balance. They may have been late on a payment in the last 2 years, or may have had a number of recent credit inquires.
679-620:
Average
Things that people commonly do to end up in this category are to open up too many new credit accounts. Perhaps these people like to save 15% off their first purchase at a department store, or they wish to take advantage of low introductory rates for balance transfers on credit cards. These people may have large debt loads from car loans or student loans. They may also have too many credit cards and/or have high balances on those cards. Being late or missing minimum payments may also contribute to these lower scores.
619-580
Poor
This group contains about 10% of Americans who likely have a combination of factors listed in the "Average" category. This group of people may have a very difficult time obtaining credit for car loans and mortgages.
Homebuyer
Vocabulary

A loan whose interest rate never changes for the life of the loan.

A long term loan that is standardized to eligible to meet FNMA (Fannie Mae) requirements. It has a fixed monthly payment for the life of the loan and is usually a 30-year period of fixed interest rate.

A loan whose interest rate is periodically adjusted to more closely coincide with current interest rates.

The cost of a mortgage stated as a
yearly rate, with all financing costs
including mortgage insurance,
and loan origination fee.

The ratio of all fixed debt, including household expenses, to gross income. Most lenders require this ration to be at 45% or less.

The mortgage company establishes an escrow account to pay property taxes and insurance during the term of the mortgage.

A down payment of less than 20%, the lender requires PMI (Private Mortgage Insurance). This protects the lender from losing money if you end up in foreclosure.

The highest price that a property is expected to bring under fair and normal market conditions.

Properties that are similar to a subject property and are used in the appraisal process. Also referred to as comps.

A form of encumbrance that holds property as security for the payment of a debt.
Facts and Tips for
Home Inspections
For most of us, our home is the biggest investment we will ever make. And before you buy, a thorough Home Inspection is key. Home Inspections are typically done before a purchase, after the property is already Under Contract. But remember, an inspection is no guarantee, nor is it a warranty.
- Home inspections typically cost around $500
- An inspection usually lasts between 3-5 hours. Let the inspector work so that they doesn't miss anything important. Then, once they're done, we will all meet for a walk-through together and you will have time to ask questions.
- It is an inspectors job to find all the things that are wrong with the home. They have a long list of things to check and they will recommend fixes based on what they find. Even if their list is long, it does not necessarily mean you are buying a lemon.
- It is a good idea to have your Inspector preform a Radon Test to know if the home you are buying will need a Radon Mitigation System. Radon is a natural occurring gas in the ground and our area can have high levels. The test costs around $100 and a Radon Mitigation System typically costs around $1,500, depending on the size of the home and the crawlspace. The radon test is done over a 48 hour period with the house completely closed up to get the "Worst Case Scenario." If your new home does require a Radon Mitigation System, it is possible that the Seller would cover part, or all, of the expense as part of the Inspection Negotiation.
Where to Start?
Start with a Whole Home Inspection. If your home is found to have mold or anything else outside of the General Inspector's Scope of expertise, ask for recommendations from your Inspector on who to contact as your next expert. Your real estate agent, Leslie Miller, is also likely to have contacts with contractors and inspectors of all kinds. Listed below are some local home inspectors you can call:
Darren Streets
Buyers Best Interest Home Inspections
406.582.7592 | 406.570.4862
darren@bbiinspection.com
Jim Sitton
Arfive Inspections
406.581.2985
406.285.4640
How Do Realtors
Get Paid?
Distribution
Once a home is listed on the MLS, the listing broker discloses the terms of the commissions to other brokers so they will bring their buyers to the listing. When the buyer's broker presents a contract to the seller, it will include a provision to collect their share of the sales commission, as offered by the listing agent on the MLS.
The Seller Pays a commission (typically 6%) to the Listing Agent.
Real Estate Agents
Nearly nine out of 10 real estate agents work on a commission and are paid only when the transaction closes. Except for the legal profession, real estate agents are the only fiduciaries and agents who work this way.
To simplify how commissions are routed, the real estate industry customarily allows all sales commissions to be paid out of the Seller's proceeds, according to the terms of the Listing Agreement.
The Listing Agent pays the Buyer's Agent out of their commission.
Brokers
According to licensing law, only licensed brokers can serve as fiduciaries. They have "agents" or licensed salespeople who work for them, but they have legal responsibilities of operating the brokerage. The salesperson license allows salespeople to serve as agents of the broker. The can negotiate contracts, but the Seller is actually negotiating with the broker by proxy. It's the broker's company name and signature on the Listing Contract.
Leslie Miller is a broker, not a salesperson, so you would be working with the broker directly.
The Low-Down on Who is
Responsible for What
Buyer:
- Review Associated Documents
- Inspection(s) and Inspection Negotiation
- Order Homeowners Insurance
- Address any other Contingencies
- Transfer Utilities
- Set up wire transfer or get Cashiers Check for funds due at closing
- Final walk-through
- Sign closing documents
- Get the keys...Welcome Home!
Title Company:
- Receive Contract & Earnest Money
- Order Title Search & gather info on property
- Examine Property
- Order Survey
- Title Insurance ordered
- Review Survey
- Order pay-off figures from Seller's existing lender
- Prepare Closing Documents
- Coordinate closing between Buyers, Sellers & Agents
- Record new Deed at County
- Fully Fund Transaction
- Congrats...and WELCOME HOME!
Mortgage Co/Lender:
- Receive Contract & Review
- Buyer Completes Loan Application
- Collect detailed info from Buyer
- Verify Buyer's info
- Review credit history
- Provide a Good Faith Estimate
- Order Appraisal
- Provide a Mortgage Commitment Letter
- Loan Package submitted to Underwriter
- Coordinate Closing between Buyers, Sellers, and Agents.
- Loan is final...WELCOME HOME!


